CONDITIONS
Medical Conditions we treat:
- Musculoskeletal Conditions
Joints & Bones
Frozen Shoulder (Adhesive Capsulitis)
Bursitis
Dislocated Shoulder
Post Surgical Rehabilitation
Knee Pain
Osteoarthritis
Condramalacia Patella
Joint Stiffness
Neck & Spine
Neck Pain & Stiffness
Spondylitis
Low Back Pain
Sciatica
Degenerative Disc Disease(DDD)
Herniated Discs(Bulging Discs)/Slipped Disc
Spondylosis
Scoliosis
Piriformis Syndrome
Posture problems
Muscles
Spasm
Fibromyalgia
Rotator Cuff Injuries
De Quervain’s tenosynovitis
Trigger Finger
- Neurological conditions
- Sports injury conditions
Low Back Pain
Low back pain can range from mild, dull, annoying pain, to persistent, severe, disabling pain in the lower back. Pain in the lower back can restrict mobility and interfere with normal functioning.
What causes low back pain?
The exact cause of low back pain can be hard to determine. In most cases, back pain may be a symptom of many different causes, including any of these:
Overuse, strenuous activity, or improper use (such as repetitive or heavy lifting, exposure to vibration for prolonged periods of time)
- Injury
- Degeneration of vertebrae (often caused by stresses on the muscles and ligaments that support the spine, or the effects of aging)
- Infection
- Abnormal growth (tumor)
- Obesity (often increases weight on the spine and pressure on the disks)
- Poor muscle tone in the back
- Muscle tension or spasm
- Sprain or strain
- Ligament or muscle tears
- Joint problems (such as spinal stenosis)
- Smoking
- Protruding or herniated (slipped) disk
- Disease (such as osteoarthritis, spondylitis, compression fractures)
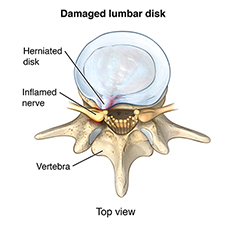
What are the symptoms of low back pain?
Low back pain is classified as acute (or short term) and chronic. Acute low back pain lasts from a few days to a few weeks. Most acute low back pain will resolve on its own. Chronic low back pain lasts for more than 3 months and often gets worse. The cause of chronic low back pain can be hard to find.
These are the most common symptoms of low back pain. Symptoms may include discomfort or pain in the lower back that is:
- Aching
- Burning
- Stabbing
- Sharp or dull
- Well-defined or vague
- The pain may radiate into one or both buttocks or even into the thigh or hip area.
The symptoms of low back pain may look like other health problems. Always see your healthcare provider for a diagnosis.
How is low back pain diagnosed?
Along with a complete medical history and physical exam, tests for low back pain may include:
X-ray. This test uses electromagnetic energy beams to make images of bones onto film.
CT scan. This imaging test uses X-rays and computer technology to make detailed images of any part of the body, including the bones, muscles, fat, and organs. CT scans are more detailed than general X-rays.
MRI. This test uses large magnets and a computer to make detailed images of organs and structures in the body.
Electromyogram (EMG). This test checks nerve and muscle function.
What can I do to prevent low back pain?
The following may help to prevent low back pain:
- Use correct lifting techniques.
- Maintain correct posture while sitting, standing, and sleeping.
- Exercise regularly (with proper stretching beforehand).
- Don’t smoke.
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Reduce stress, which may cause muscle tension.

